Scalability in Cloud Computing: Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling
If your business website or application becomes popular in the market or there is an increase in demand, you must broaden your view of user accessibility and performance. What do you do? The answer for this is usually some type of scalability of your IT infrastructure. When talking about scalability in cloud computing, you will often hear about two ways of scaling: horizontal or vertical.
In this blog post, we will look deeper into these terms and also into AWS (Amazon Web Services) scalability and which services you can use.
What is scalability?
Cloud scalability refers to the ability to increase or decrease IT resources (virtual machines, databases, networks) as needed to meet changing needs. Scalability is one of the main advantages of the cloud and the main driving force for its popularity in businesses.
Public cloud providers such as AWS (Amazon Web Services) already have all the infrastructure in place; in the past, when scaling had to be done using on-premises infrastructure, the process could take weeks or months and require capital investment.
Systems have four general areas that scalability can apply to:
- CPU
- Disk I/O
- Memory
- Network I/O
The main benefit of the scalable architecture is performance and the ability to handle bursts of traffic or heavy loads with little or no notice.
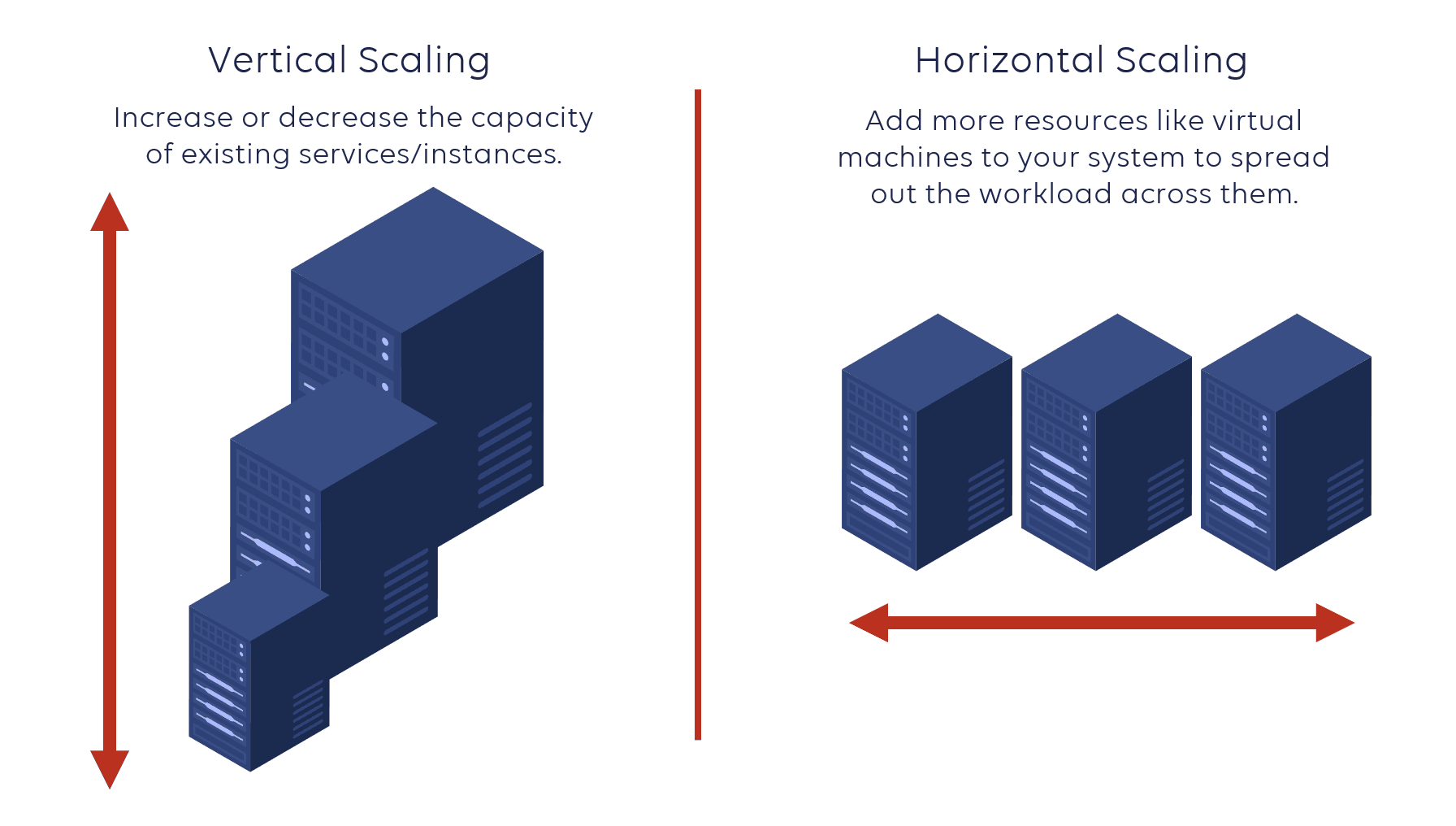
What is horizontal scaling?
To scale horizontally (scaling in or out), you add more resources like virtual machines to your system to spread out the workload across them. Horizontal scaling is especially important for companies that need high availability services with a requirement for minimal downtime.

Benefits of horizontal scaling
Horizontal scaling increases high availability because as long as you are spreading your infrastructure across multiple areas, if one machine fails, you can just use one of the other ones.
Because you’re adding a machine, you need fewer periods of downtime and don’t have to switch the old machine off while scaling. There may never be a need for downtime if you scale effectively.
And here are some simpler advantages of horizontal scaling:
- Easy to resize according to your needs
- Immediate and continuous availability
- Cost can be linked to usage and you don’t always have to pay for peak demand
Disadvantages of horizontal scaling
The main disadvantage of horizontal scaling is that it increases the complexity of the maintenance and operations of your architecture, but there are services in the AWS environment to solve this issue.
- Architecture design and deployment can be very complicated
- A limited amount of software that can take advantage of horizontal scaling
What is vertical scaling?
Through vertical scaling (scaling up or down), you can increase or decrease the capacity of existing services/instances by upgrading the memory (RAM), storage, or processing power (CPU). Usually, this means that the expansion has an upper limit based on the capacity of the server or machine being expanded.

Vertical scaling benefits
- No changes have to be made to the application code and no additional servers need to be added; you just make the server you have more powerful or downsize again.
- Less complex network – when a single instance handles all the layers of your services, it will not have to synchronize and communicate with other machines to work. This may result in faster responses.
- Less complicated maintenance – the maintenance is easier and less complex because of the number of instances you will need to manage.
Vertical scaling disadvantages
- A maintenance window with downtime is required – unless you have a backup server that can handle operations and requests, you will need some considerable downtime to upgrade your machine.
- Single point of failure – having all your operations on a single server increases the risk of losing all your data if a hardware or software failure were to occur.
- Upgrade limitations – there is a limitation to how much you can upgrade a machine/instance.
Horizontal vs. vertical scaling
In the cloud, you will usually use both of these methods, but horizontal scaling is usually considered a long-term solution, while vertical scaling is usually considered a short-term solution. The reason for this distinction is that you can usually add as many servers to the infrastructure as you need, but sometimes hardware upgrades are just not possible anymore.
Both horizontal and vertical scaling have their benefits and limitations. Here are some factors to consider:
- Upgradability and flexibility – if you run your application layer on separate machines (horizontally scaled), they are easier to decouple and upgrade without downtime.
- Worldwide distribution – if you plan to have national or global customers, it is unreasonable to expect them to access your services from one location. In this case, you need to scale resources horizontally.
- Reliability and availability – horizontal scaling can provide you with a more reliable system. It increases redundancy and ensures that you are not dependent on one machine.
- Performance – sometimes it’s better to leave the application as is and upgrade the hardware to meet demand (vertically scale). Horizontal scaling may require you to rewrite code, which can add complexity.
Scalability on AWS
AWS as a platform has scalability built-in. They offer many services and features that can help set up your application to scale up or down depending on the resource requirements.
Below you can find a list of services that are commonly used for horizontal or vertical scaling or both.
Horizontal scaling in AWS
A simple example of horizontal scaling in AWS Cloud is adding/removing Amazon EC2 instances from your application architecture behind Elastic Load Balancer. A simple example architecture is provided below.
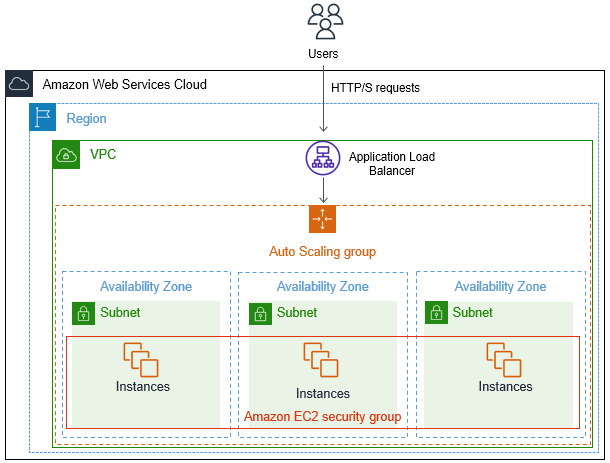
Here is a list of AWS services and features that can help you with horizontal scaling:
1. Regions & Availability Zones
Regions and Availability Zones enable you to scale applications horizontally across data centers and geographic regions to ensure resiliency and proximity to users.
An Availability Zone consists of one or more data centers in a geographic area, which are physically separated from each other in terms of power, network, and security. The best practice is to distribute the workload across multiple Availability Zones to reduce the risk of hardware or facility failure.
A Region is a geographic area that contains two or more Availability Zones. Scaling the application across multiple regions helps ensure the best experience for your users.
2. Elastic Load Balancer
This service is used to automatically distribute incoming application traffic across multiple targets (EC2 instances, Lambda functions, etc.)
This service is divided into the two of the most used types:
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) – best suited for load balancing of HTTP and HTTPS traffic. They operate at Layer 7 and are application-aware. They do have some default limits set, some of which can be raised on request. The default limits include 1000 Targets per ALB, 50 listeners per ALB, 50 ALBs per region and 3,000 targets per region.
- Network Load Balancer (NLB) – Network Load Balancers operate at Layer 4, the transport layer. They can load balance tens of millions of requests per second at very low latency. As for ALB, you can have 50 NLBs per region and 3000 target groups per region by default.
3. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling enables fleets of EC2 instances to scale based on application traffic or demand.
It’s defined as an Auto Scaling group by the launch template on the Elastic Load Balancer. The launch template defines the minimum and the maximum number of EC2 instances in the group, as well as the indicators that trigger the launch of new instances. These triggers can be based on instance health checks, CPU load, incoming or outgoing network traffic, or the number of load balancer requests per target.
4. AWS Auto Scaling
AWS Auto Scaling is a service in the AWS Cloud environment which enables you to configure scaling for selected AWS services that are part of your application in minutes. You can be sure that you’ll always have enough resources/instances to handle your application load, no matter how greatly or suddenly traffic may spike. Learn more in our blog post: AWS Auto Scaling: Everything That You Need to Know
5. AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk enables you to create simple web applications that scale automatically without worrying about any underlying infrastructure such as Elastic Load Balancers, EC2 instances, and databases. It supports web applications written in Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker on familiar servers such as Apache, Nginx, Passenger, and IIS.
6. Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Amazon ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service. Containerized applications lend themselves very well to horizontal scaling. By default, ECS can manage 10,000 clusters per region, with 1,000 services per cluster.
Vertical scaling in AWS
Every AWS service mentioned below supports vertical scaling, but you are also able to horizontally scale these services using Availability Zones and Regions.
1. Amazon EC2 Instance
An EC2 instance is a virtual server in the AWS Cloud. For any service in the AWS environment, the EC2 instances are behind it as virtual machines. AWS has a huge range of EC2 instances for different workload types.
The maximum for vertical scaling of CPU is the Compute Optimized EC2 instance (c5d.metal) that has 96 vCPUs while the largest Memory Optimized instance (u-24tb1.metal) has 24TB of memory.
2. AWS Lambda
Lambda is a computing service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. Just upload your code and start a Lambda function. Lambda then scales automatically. Every time an event notification is received for your function, AWS Lambda quickly locates free capacity within its compute fleet and runs your code.
3. EBS Volumes
EBS Volumes are the hard disk drive volumes that can be attached to EC2 instances. A single General Purpose (GP2) EBS volume can scale to 16TB and 10,000 IOPS. A Provisioned IOPS EBS volume can scale to 16TB and 64,000 IOPS.
4. EFS Volumes
EFS or Elastic File System is a shared storage volume that can be mounted via NFS to an operating system, enabling multiple instances to see the same disk volume. With EFS Storage you only pay for what you consume, but an EFS volume is virtually infinitely scalable.
5. Amazon S3
S3 or Simple Storage Service is an AWS object storage solution for documents, videos, audio files, etc.
S3 has almost unlimited scalability, and you only pay for the content stored in it. The size of a single object can be up to 5TB, and there is no limit to the number of objects that can be stored in the bucket.
6. Amazon DynamoDB
DynamoDB is a fast, highly reliable, and cost-effective NoSQL database service. DynamoDB delivers automatic scaling of throughput and storage based on your previously set capacity by monitoring the performance usage of your application.
7. Amazon RDS
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) makes it easy to operate and scale a relational database in the AWS Cloud. With RDS Storage Auto Scaling, you simply set your desired maximum storage limit, and this feature takes care of the rest.
Conclusion
Creating a fully scalable system and infrastructure can be a large task that requires planning, testing, and more testing. If you already have an application in place, splitting up that system can be a problematic process that may require code changes, software updates, and more monitoring.
Our certified AWS architects will provide you with recommendations and guidance for designing and deploying high-availability architectures on AWS.
An AWS Solutions Architect with over 5 years of experience in designing, assessing, and optimizing AWS cloud architectures. At Stormit, he supports customers across the full cloud lifecycle — from pre-sales consulting and solution design to AWS funding programs such as AWS Activate, Proof of Concept (PoC), and the Migration Acceleration Program (MAP).


